Welcher Stoffwechselweg ist sowohl bei der Zellatmung als auch bei der Fermentation üblich?

Welcher Stoffwechselweg ist sowohl bei der Zellatmung als auch bei der Fermentation üblich?
Der Stoffwechsel ist ein lebenswichtiger Prozess in allen lebenden Zellen, bei dem Kohlenhydrate, Fette und Proteine in Energie umgewandelt werden. Es gibt verschiedene Stoffwechselwege, die je nach den vorhandenen Bedingungen und den Anforderungen der Zelle aktiviert werden. Bei der Zellatmung und Fermentation handelt es sich um zwei wichtige Stoffwechselwege zur Energiegewinnung in Zellen. Ein bestimmter Stoffwechselweg ist bei beiden Prozessen häufig anzutreffen und wird im Folgenden näher erläutert.
Die Zellatmung
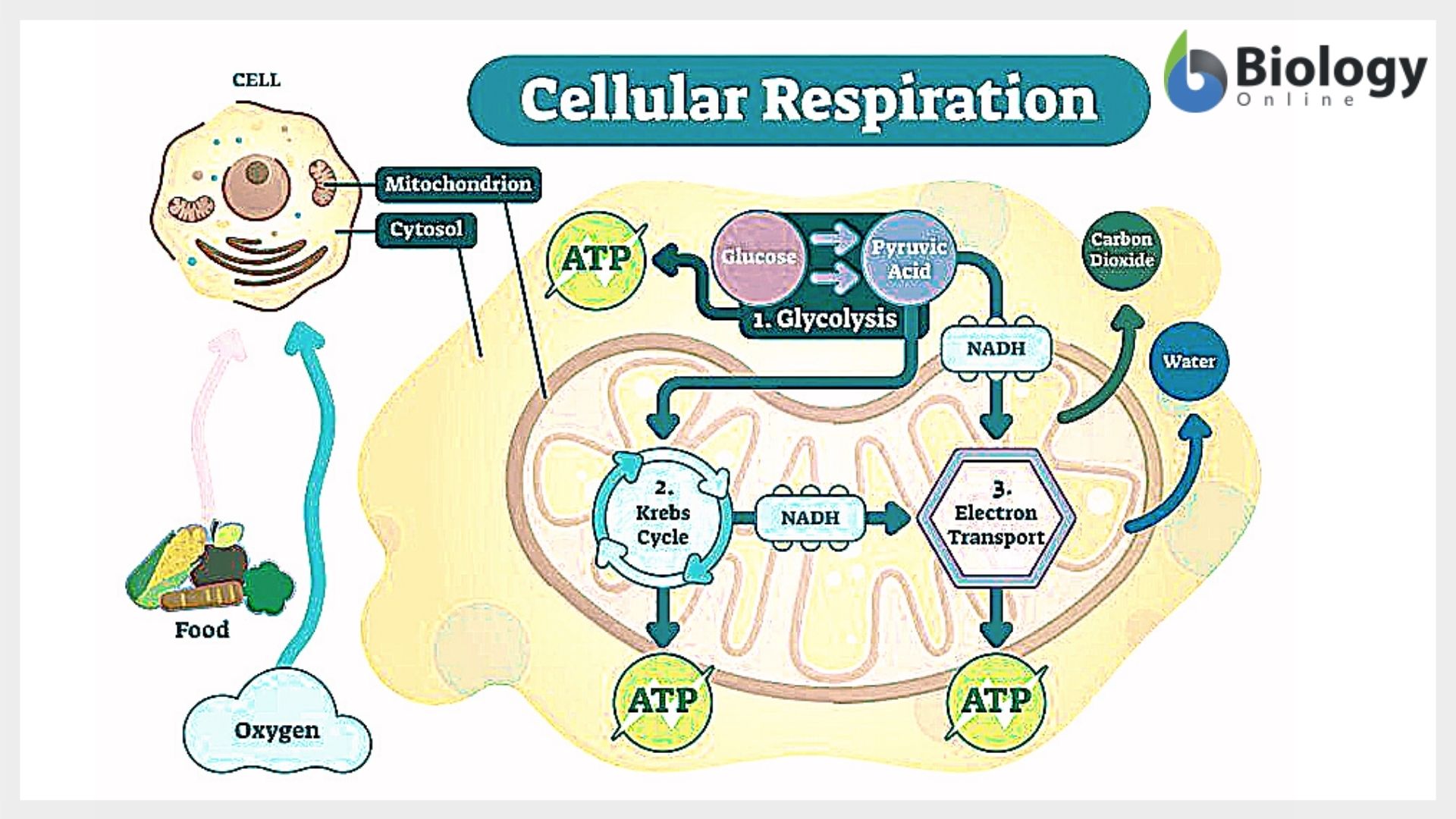
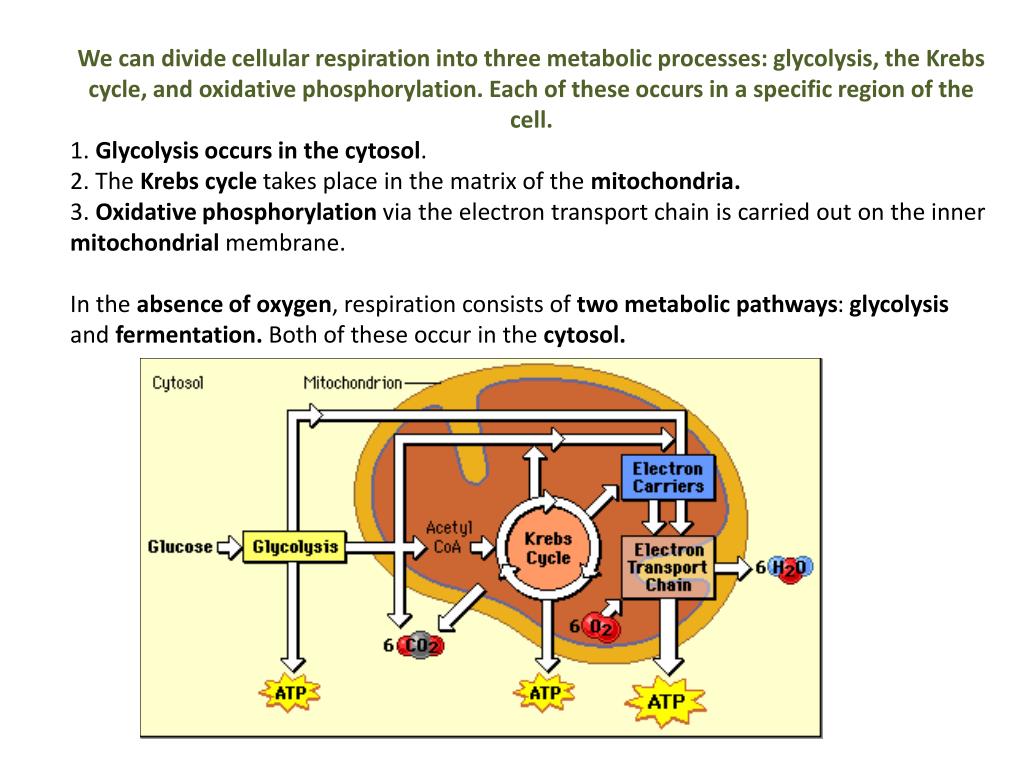
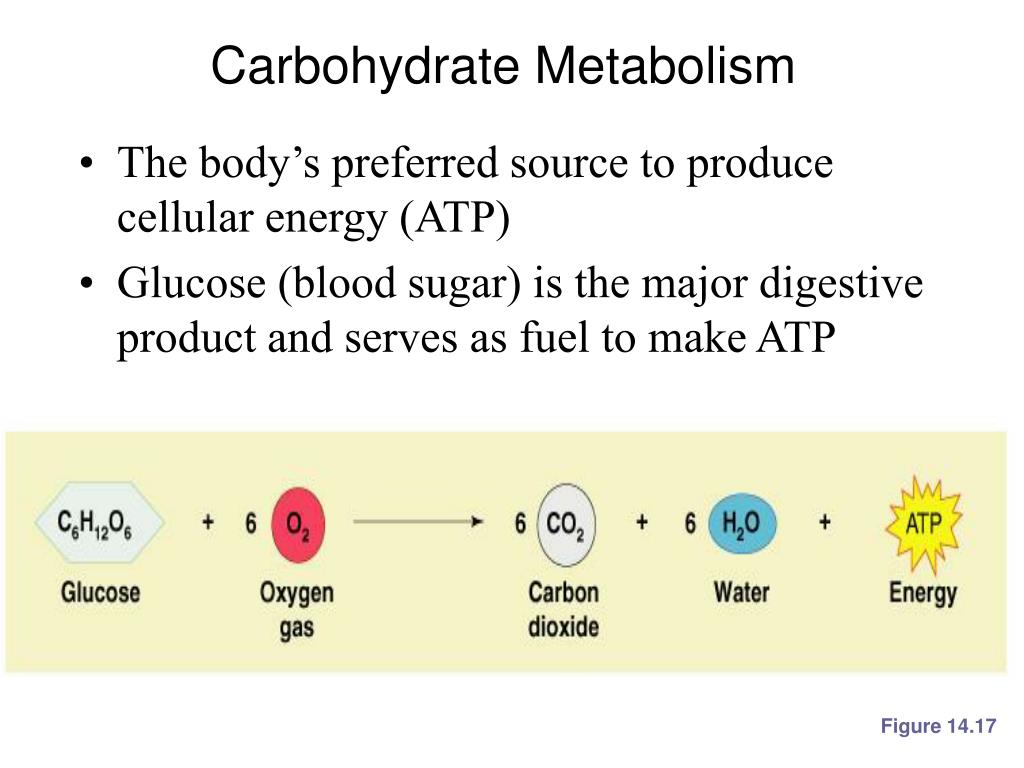
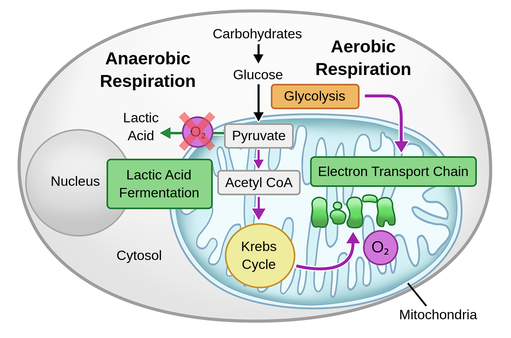
Die Zellatmung ist ein biochemischer Prozess, bei dem organische Moleküle wie Glukose mit Hilfe von Sauerstoff zu Kohlendioxid und Wasser abgebaut werden. Dieser Prozess findet in den Mitochondrien statt, den sogenannten Kraftwerken der Zelle. Während der Zellatmung werden große Mengen an Energie in Form von Adenosintriphosphat (ATP) produziert, das als Energiequelle für lebenswichtige Zellfunktionen dient.
Die Fermentation
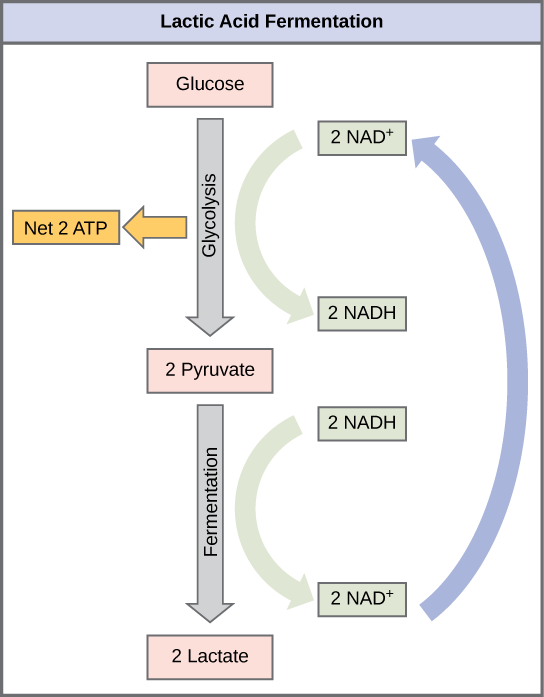
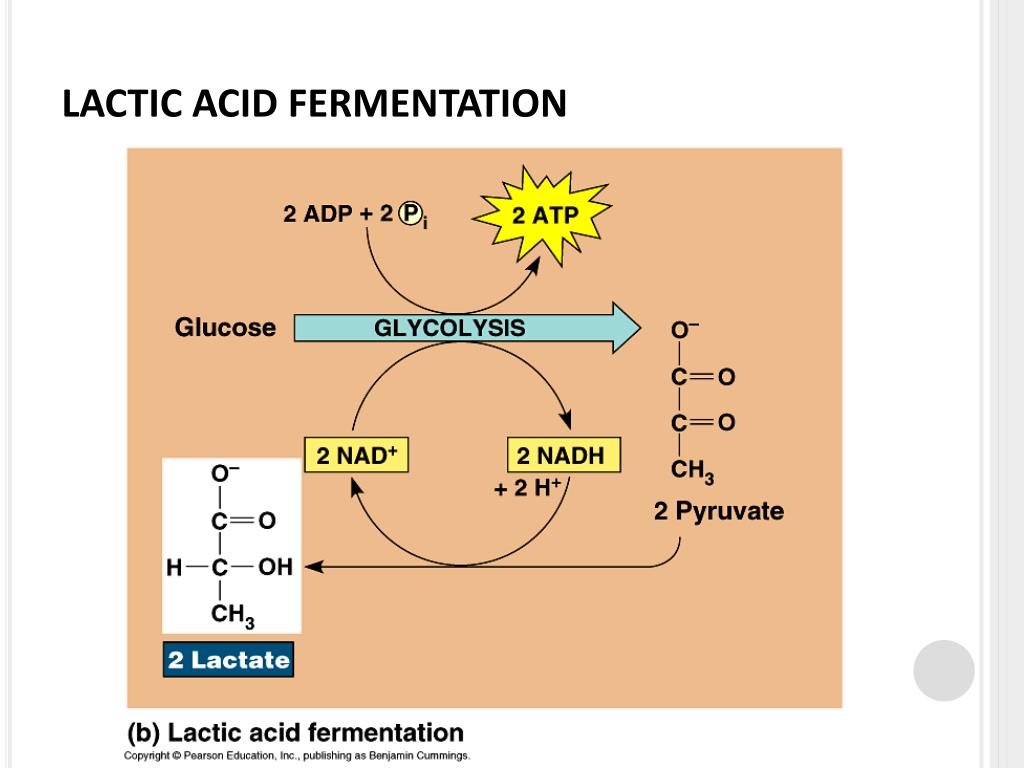
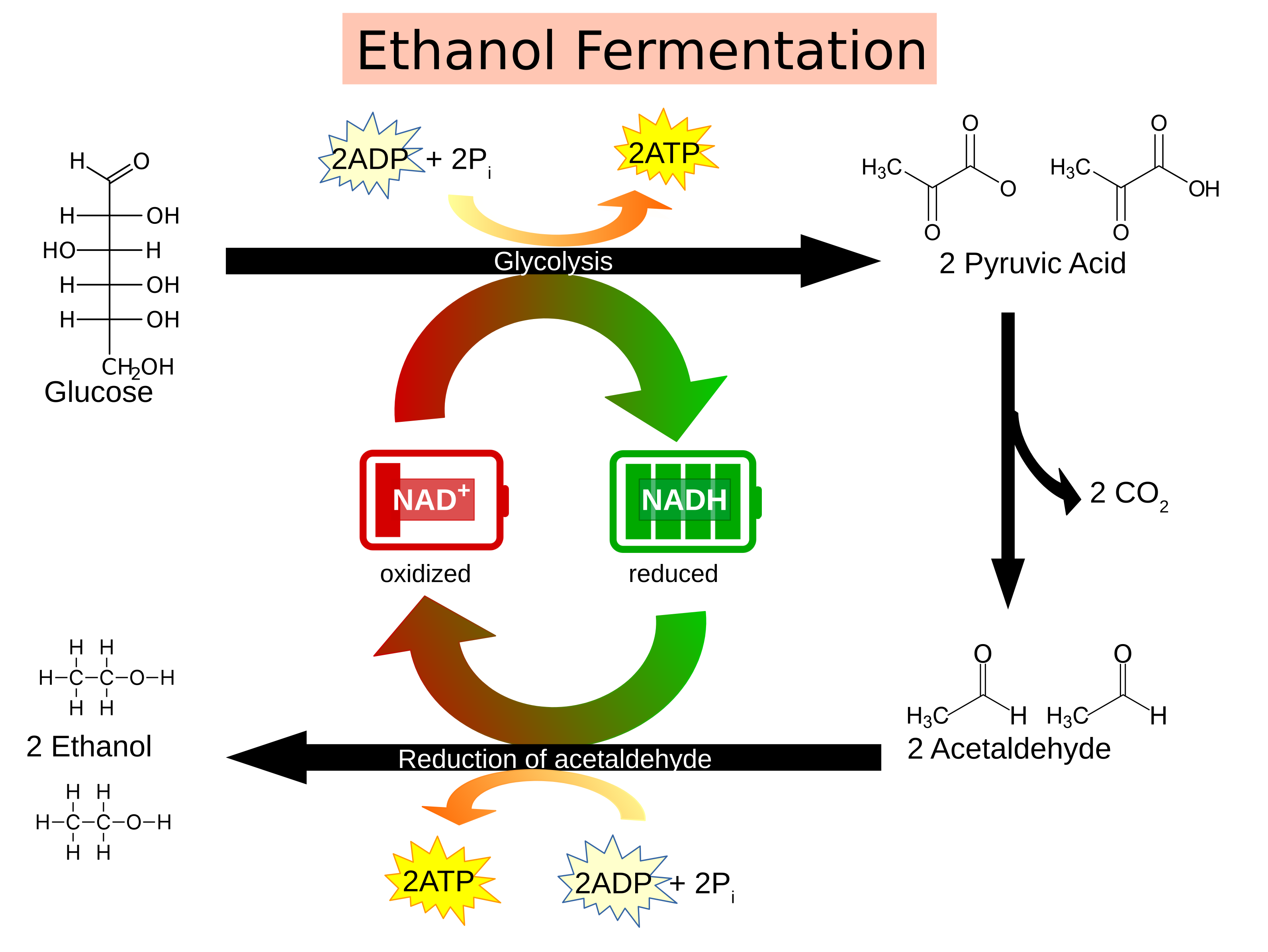
Die Fermentation ist ein anaerober Prozess, bei dem organische Moleküle wie Glukose zu einfachen Verbindungen abgebaut werden, ohne dass Sauerstoff benötigt wird. Im Gegensatz zur Zellatmung erfolgt die Fermentation in den Cytoplasmen der Zellen. Die Fermentation ist ein energieerzeugender Prozess, der unter anaeroben Bedingungen auftritt, wie zum Beispiel bei einigen Bakterien oder in Muskelzellen während intensiver körperlicher Aktivität.
Der gemeinsame Stoffwechselweg
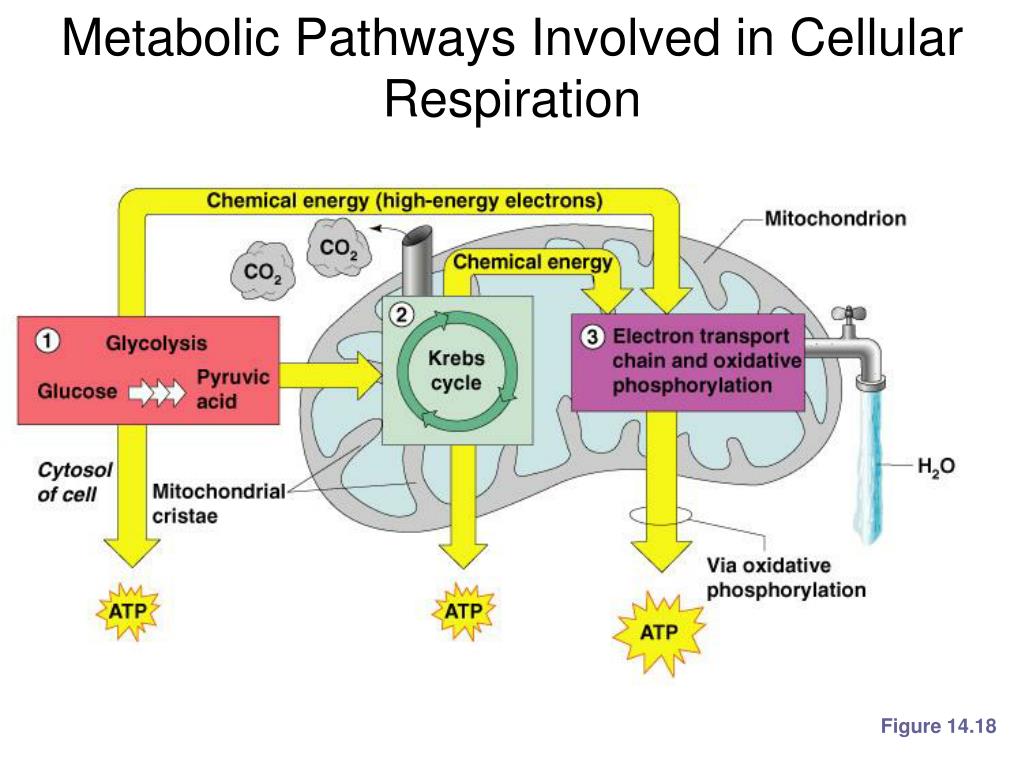
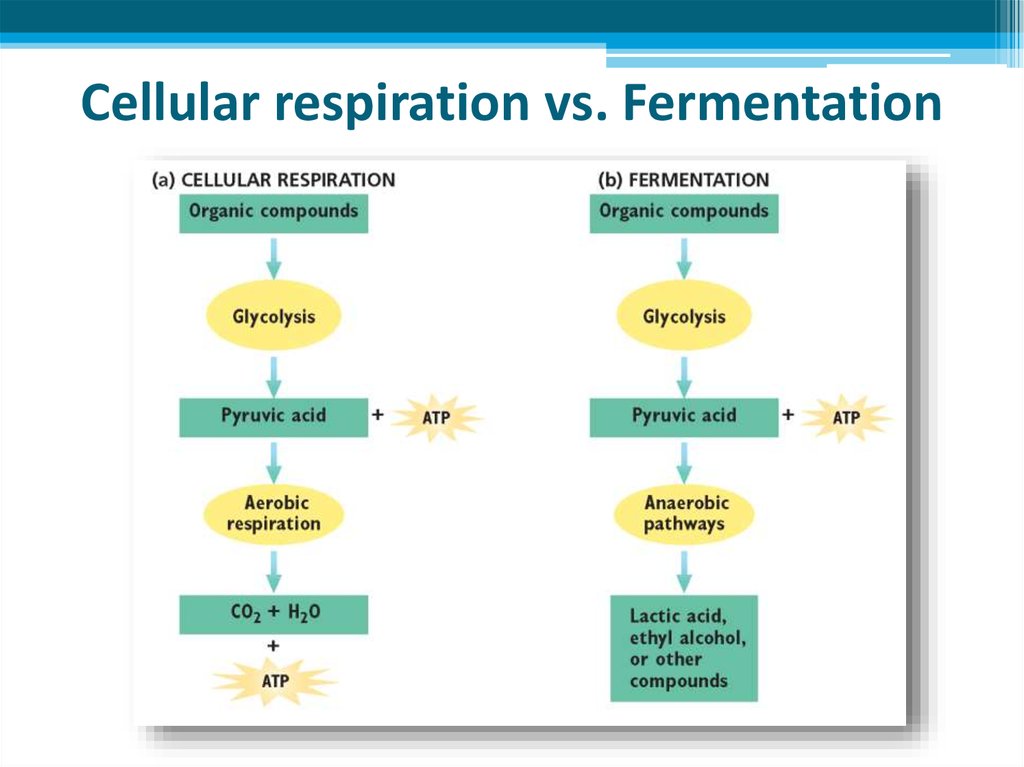
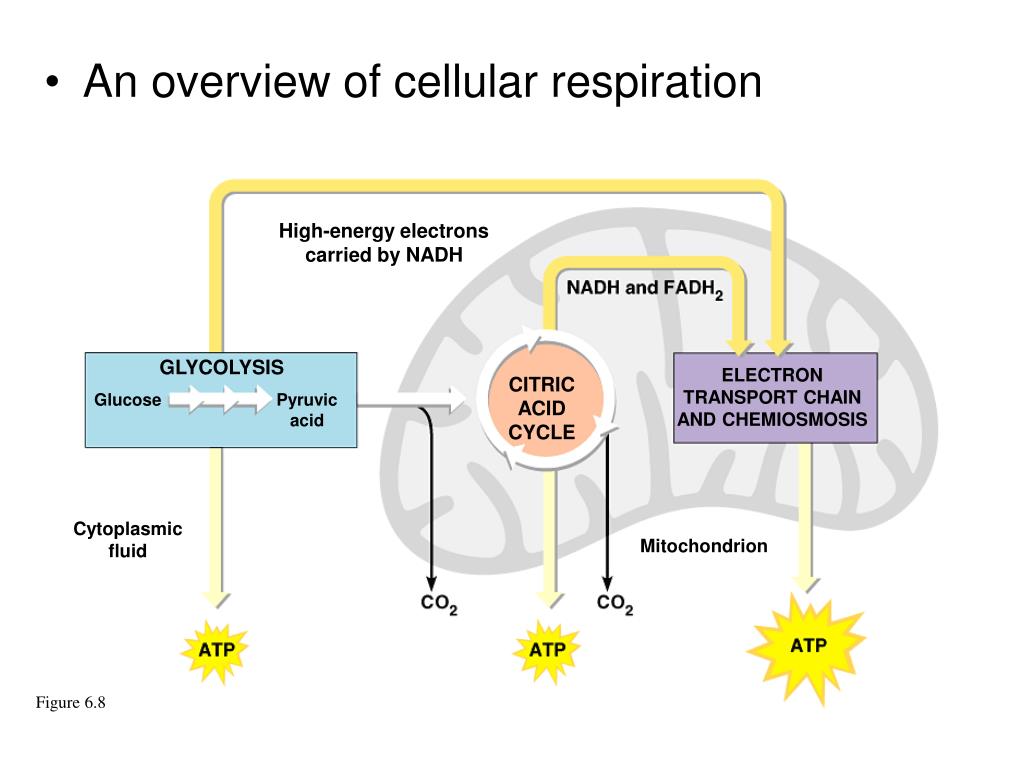
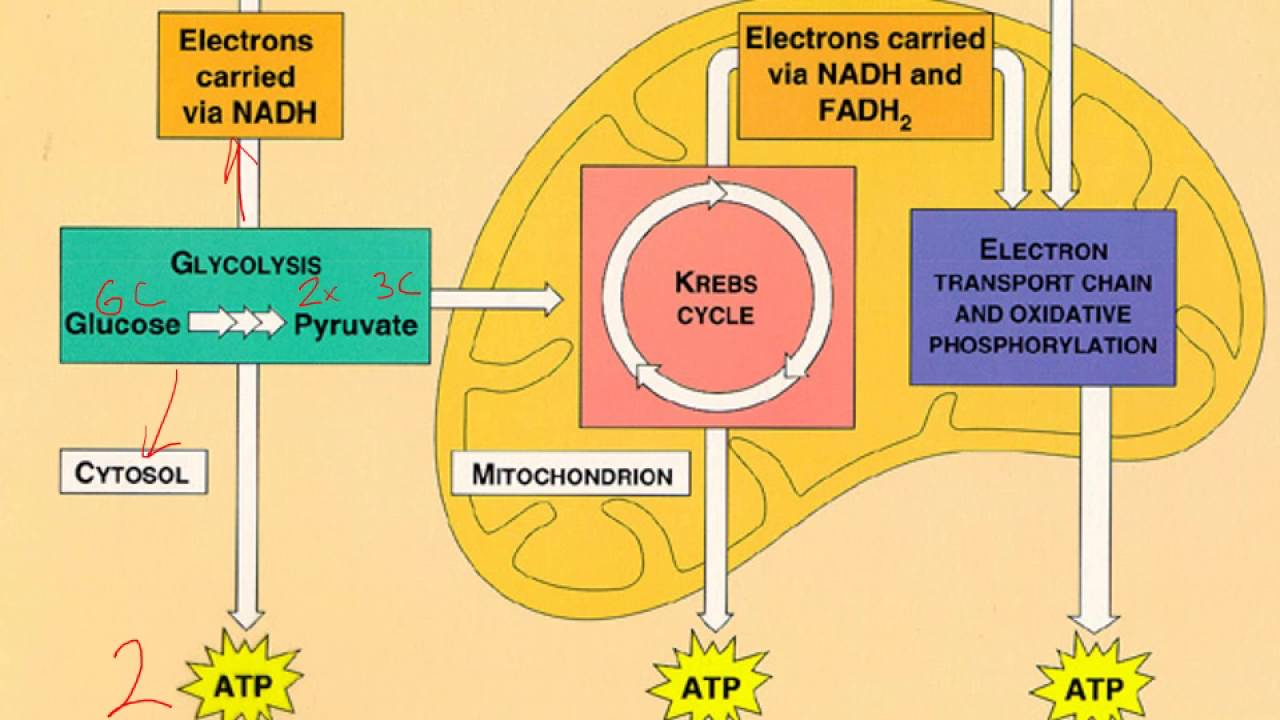
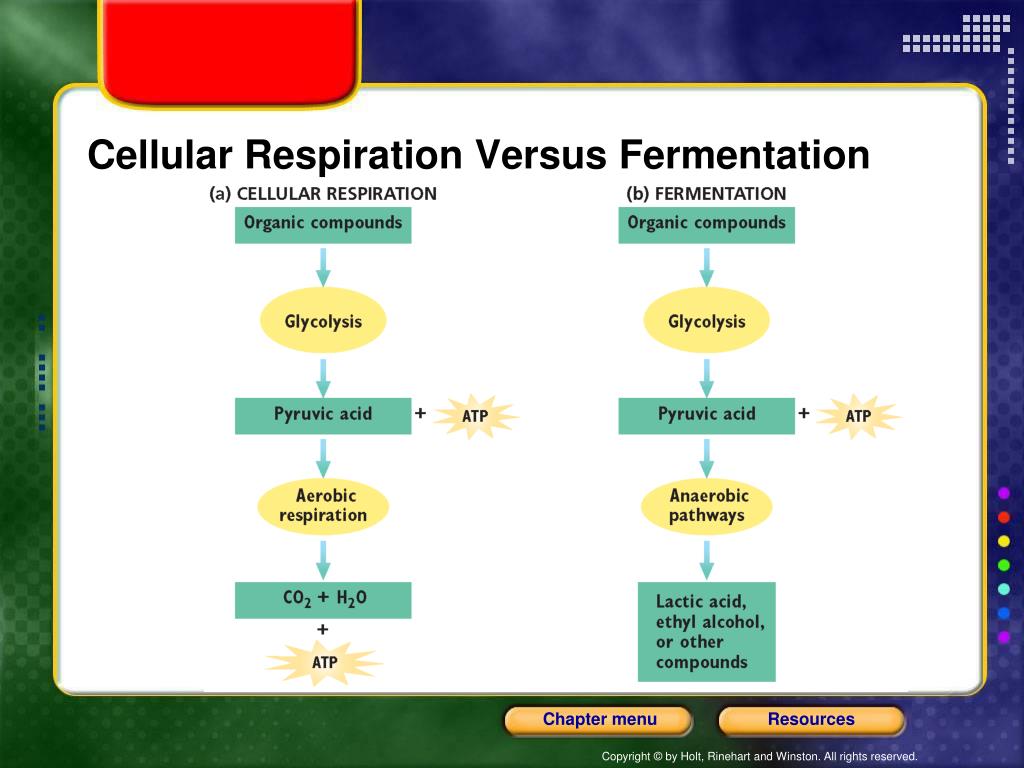
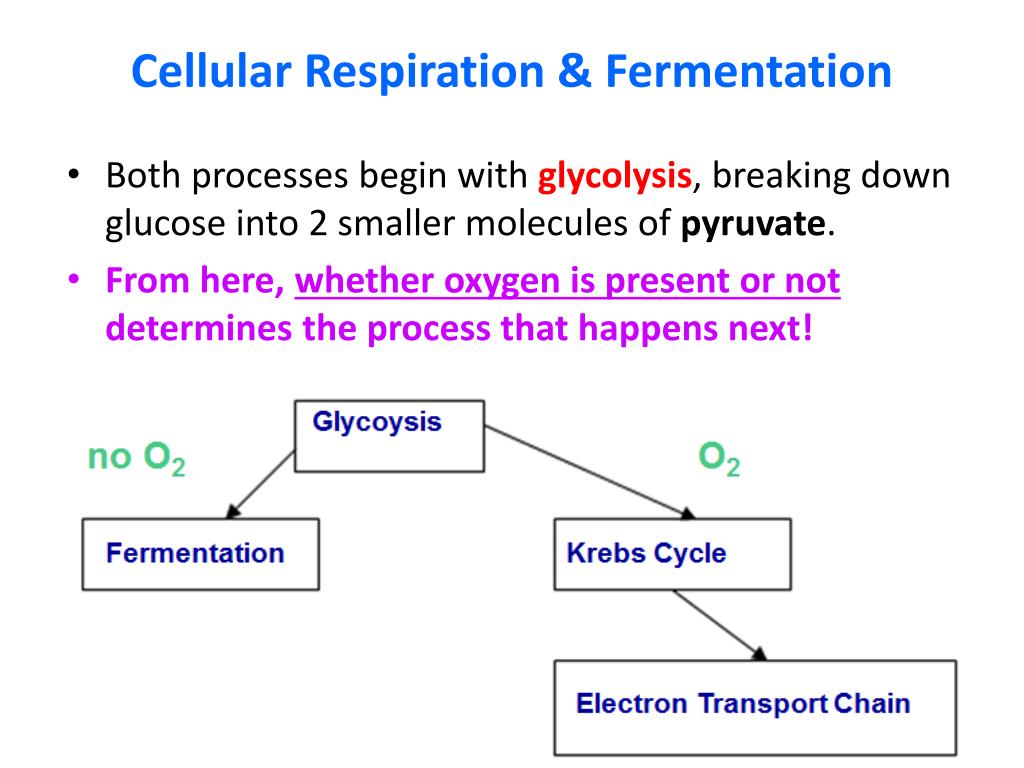
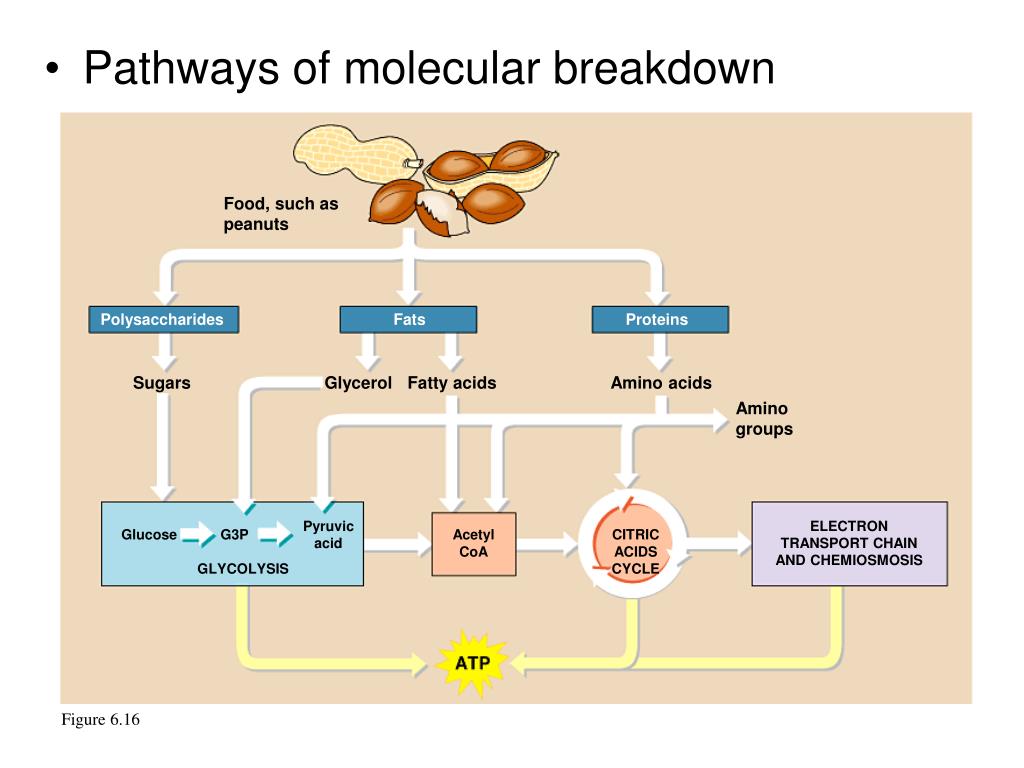
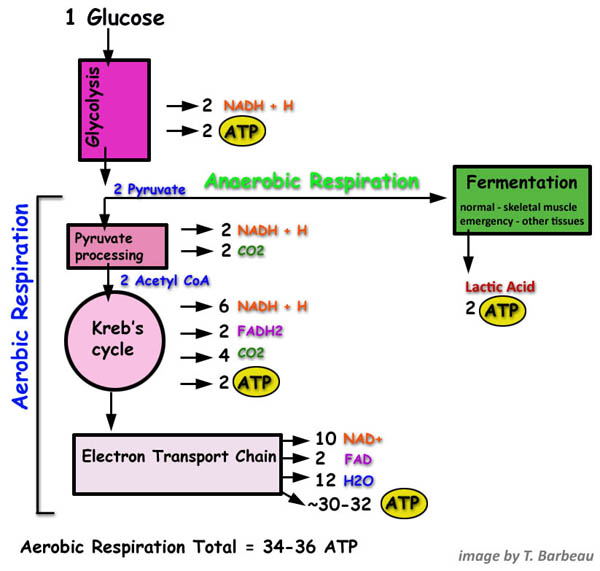
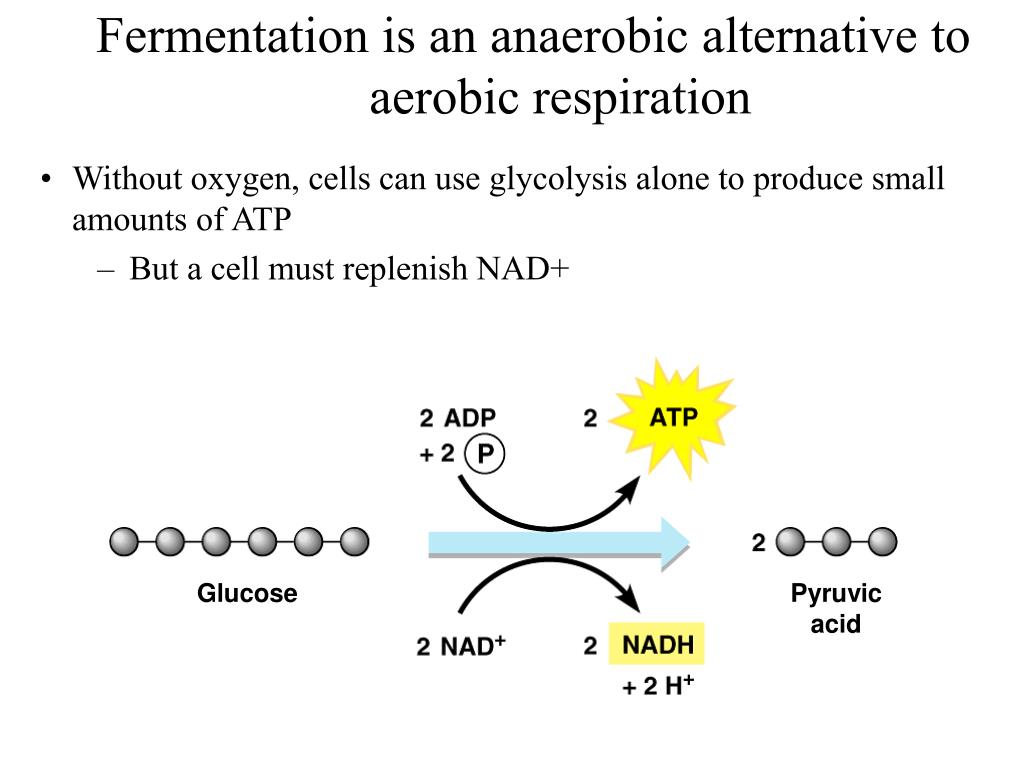
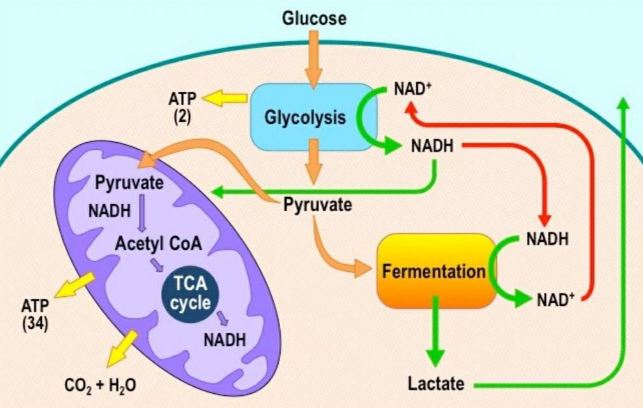
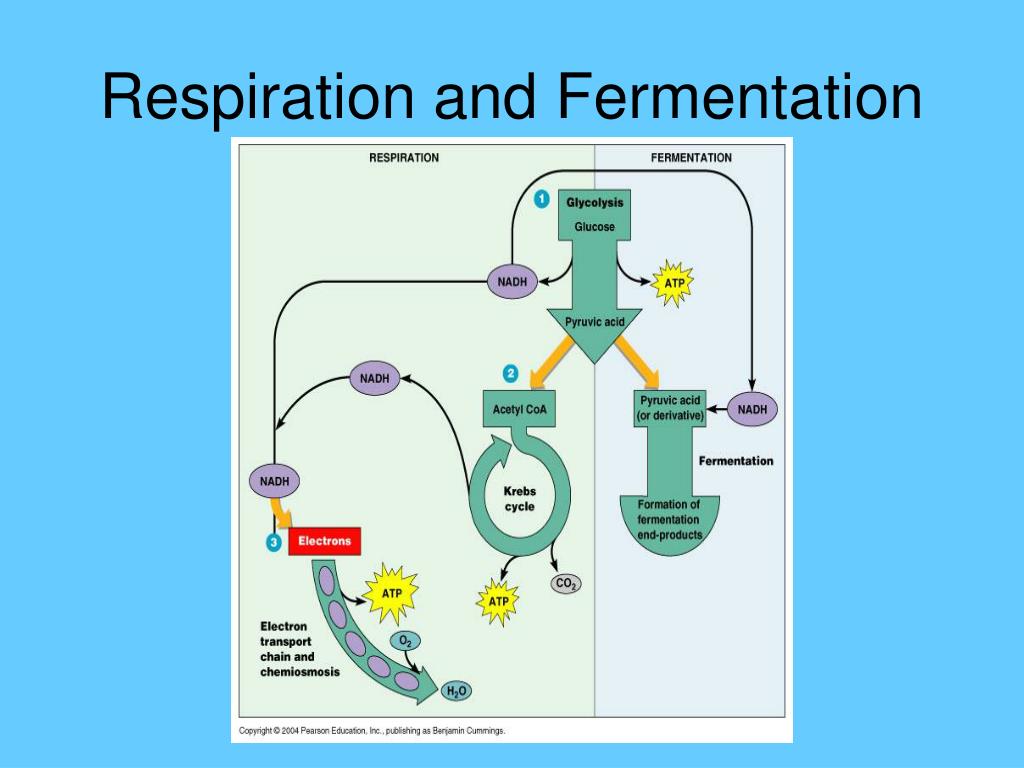
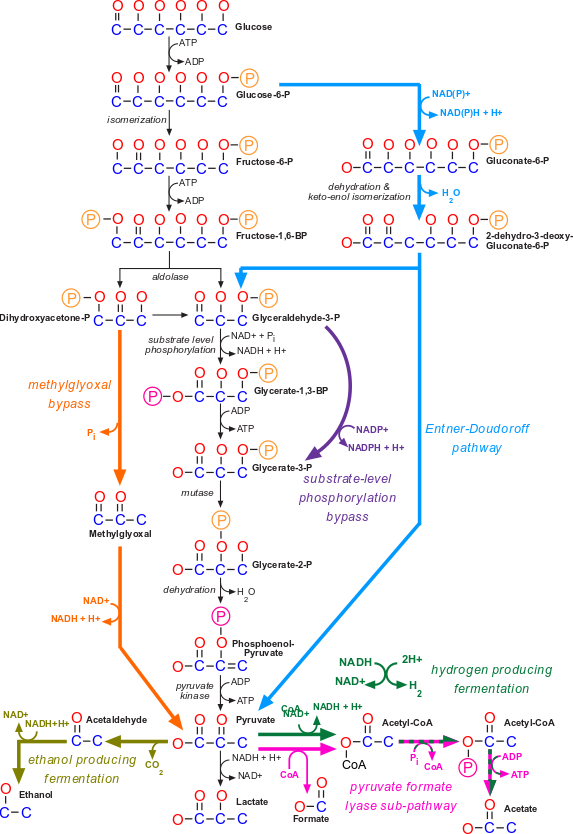
Der glykolytische Stoffwechselweg ist ein gemeinsamer Stoffwechselweg, der sowohl in der Zellatmung als auch in der Fermentation vorkommt. Dieser Stoffwechselweg ist unabhängig von Sauerstoff und beginnt mit der Glykolyse, bei der ein Molekül Glukose zu zwei Molekülen Pyruvat abgebaut wird. Die Glykolyse findet im Cytoplasma der Zelle statt und ist der erste Schritt in der Energiegewinnung aus Glukose.
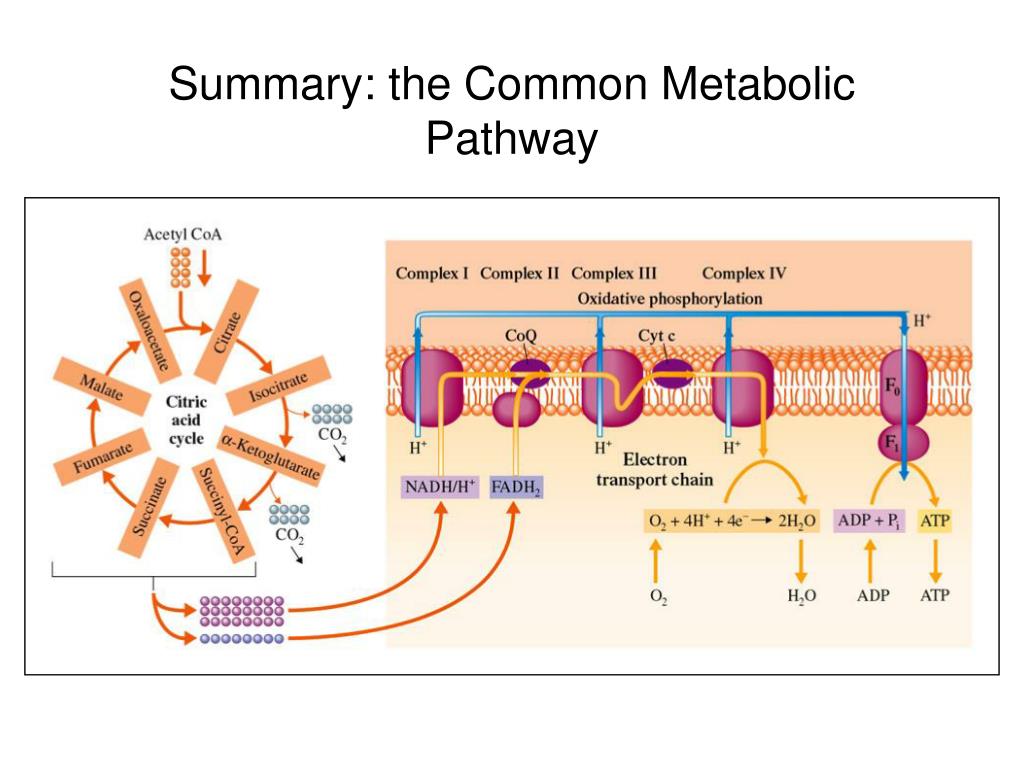
Während der Glykolyse werden zwei Moleküle ATP produziert, aber es wird keine weitere Energie aus Glukose freigesetzt. Bei der Zellatmung wird der glykolytische Stoffwechselweg fortgesetzt, indem das Pyruvat in den Mitochondrien oxidiert wird. Dieser oxidative Stoffwechselweg ermöglicht die Produktion großer Mengen an ATP durch Prozesse wie den Citratzyklus und die oxidative Phosphorylierung.
In der Fermentation hingegen endet der glykolytische Stoffwechselweg mit der Produktion von Milchsäure, Alkohol oder anderen organischen Verbindungen. Obwohl die Fermentation viel weniger ATP produziert als die Zellatmung, ermöglicht sie dennoch eine begrenzte Energiegewinnung ohne Sauerstoff.

Unterschiede zwischen Zellatmung und Fermentation
Obwohl beide Stoffwechselwege den glykolytischen Stoffwechselweg gemeinsam haben, unterscheiden sie sich hinsichtlich des Energieertrags und der Endprodukte. Die Zellatmung ist ein effizienterer Stoffwechselweg, der große Mengen an ATP produziert und dabei Kohlendioxid und Wasser als Endprodukte erzeugt. Die Fermentation ist hingegen ein weniger effizienter Weg zur Energiegewinnung, der geringere Mengen an ATP erzeugt und als Endprodukte Stoffe wie Milchsäure oder Alkohol produziert.
Die Bedeutung des glykolytischen Stoffwechselwegs
Der glykolytische Stoffwechselweg ist für Zellen von großer Bedeutung, da er auch unter anaeroben Bedingungen ATP produzieren kann. Dies ist besonders wichtig, wenn die Sauerstoffversorgung beeinträchtigt ist oder nicht ausreicht, beispielsweise bei intensivem Training oder in Geweben mit begrenztem Sauerstoffzugang. Der glykolytische Weg kann daher als Überlebensmechanismus dienen und den Zellen ermöglichen, auch unter suboptimalen Bedingungen Energie zu generieren.
PPT

Connections between cellular respiration and other pathways

Cellular Respiration & Fermentation

AP Biology- Cellular Respiration + Fermentation Diagram

Cellular Respiration
How Is Atp Synthesized In Fermentation

Overview of the major steps of Cellular Respiration! Glycolysis, Krebs ...
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration
PPT
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
6.5: Fermentation

Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration and Fermentation

which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular ...
PPT
PPT
Cellular Respiration & Fermentation

respiration pathway

Fermentation, Lactic acid, Anaerobic Pathways

Difference between cellular respiration and fermentation
PPT
PPT
Health Science Academy [licensed for non-commercial use only] / Chapter ...
PPT

Metabolic pathways of fermentation that can be exploited through the ...
Fermentation

Difference Between Fermentation and Respiration
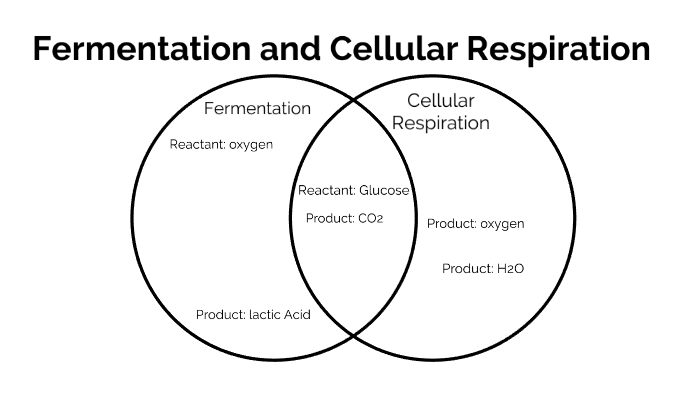
fermentation and cellular respiration venn diagram by Annika E.

(4) Cellular respiration review (article)

Metabolic pathways in the glycerol fermentation of C. pasteurianum ...
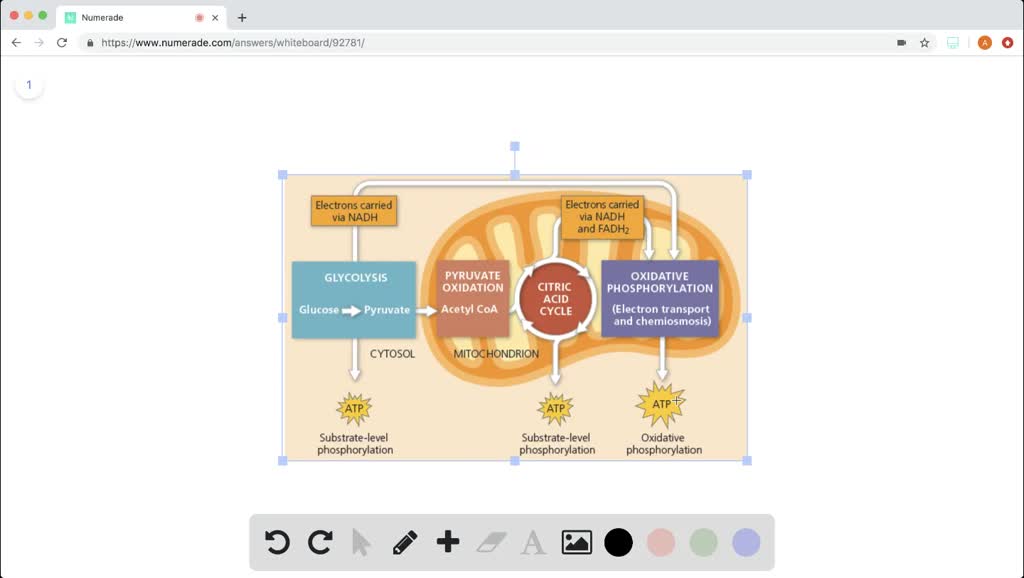
SOLVED:Which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and ...

biochemistry
Metabolism 4: Anaerobic Cellular Respiration: Main Pathway and Applications
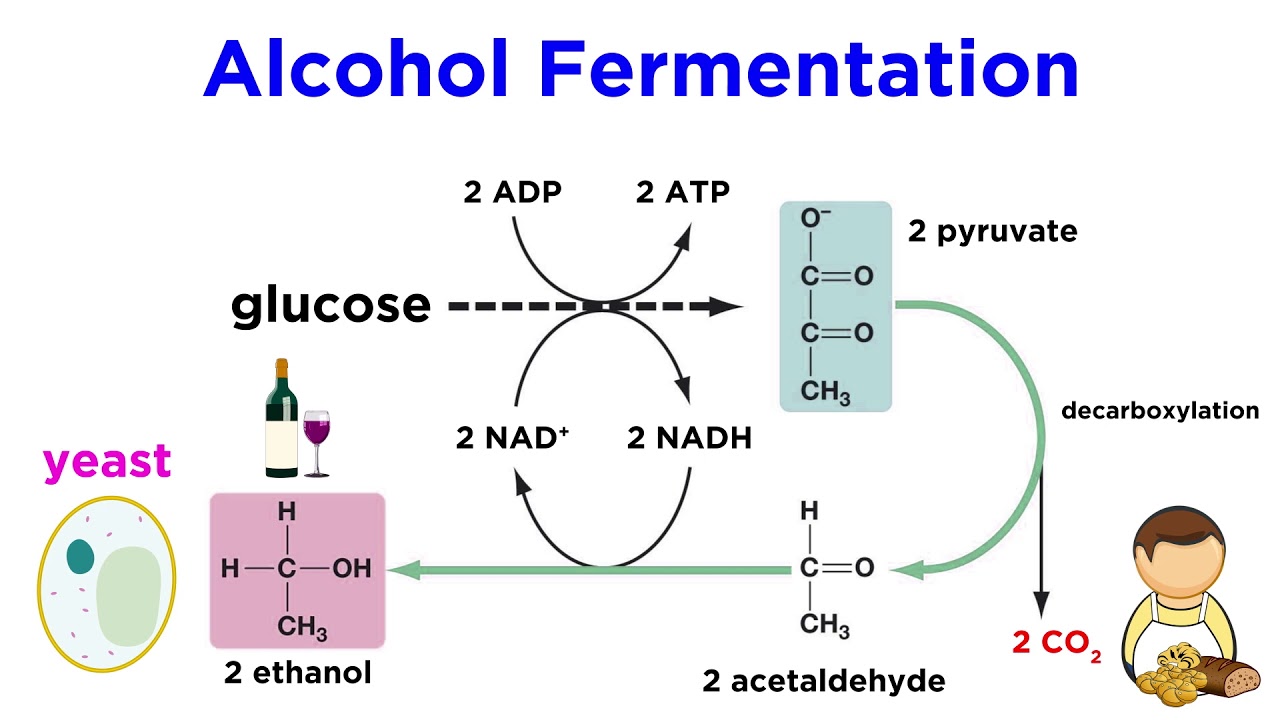
Anaerobic Respiration and Fermentation

Metabolic pathways in ABE fermentation by clostridia. The pink area ...

The Efficacy Of Photosynthesis Vs Fermentation
Which metabolic pathway is common to both cellular respiration and ...

Possible metabolic pathway for glycerol fermentation by C ...

715 Cellular Respiration Images, Stock Photos & Vectors
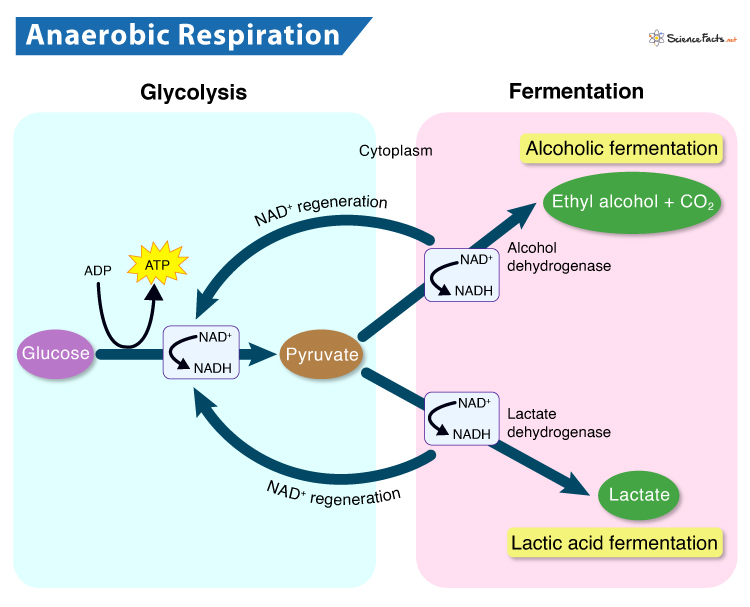
Anaerobic Respiration: Definition, Equation, Steps, & Examples

Connections between cellular respiration and other pathways
PPT
Cellular respiration
Fermentation: An Anaerobic Pathway in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes

e Simplified possible metabolic pathways during anaerobic fermentation ...
Respiration vs. Fermentation
How do aerobic respiration and fermentation compare with respect to the ...
PPT
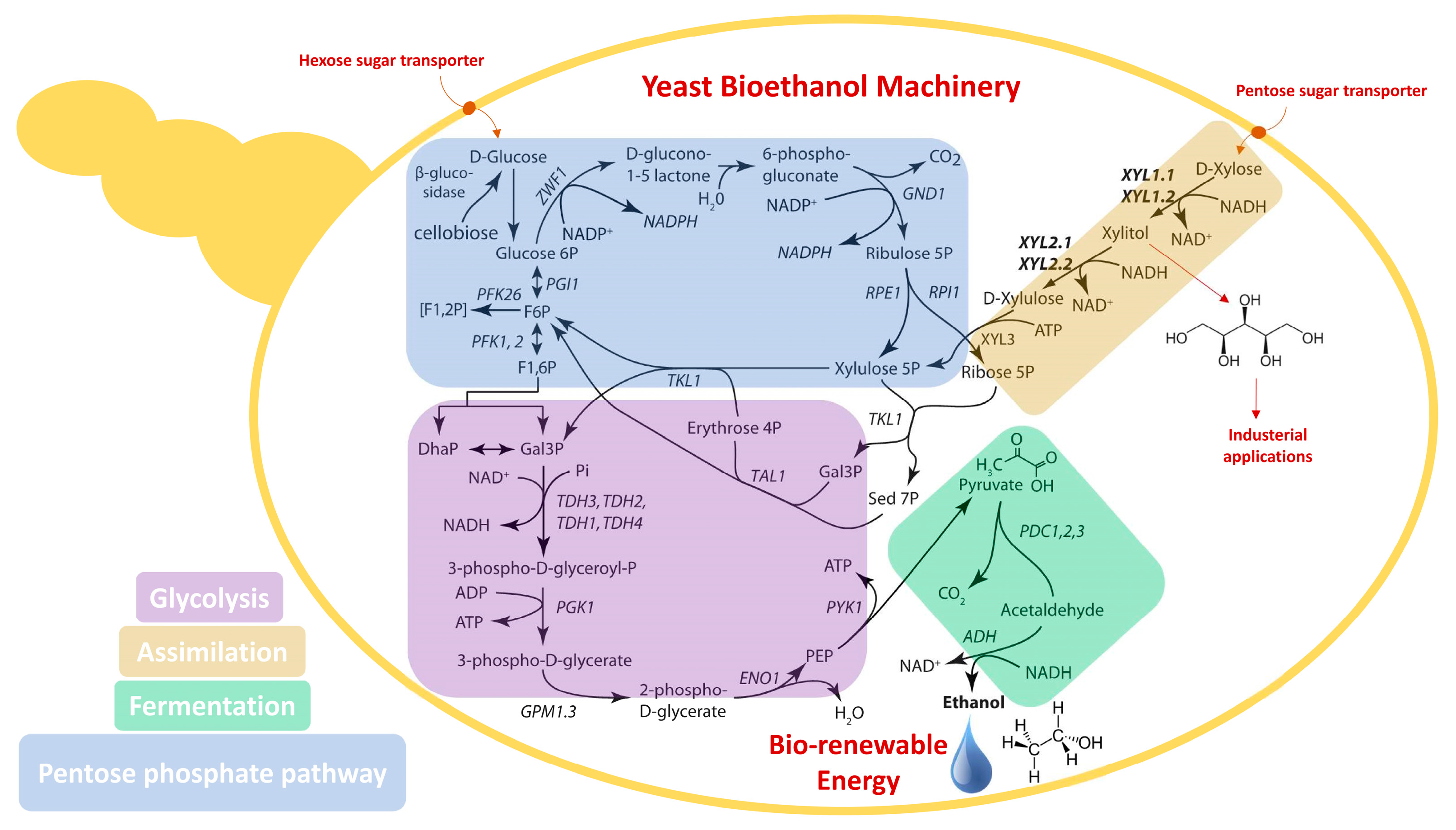
Fermentation
Metabolic Pathways

Biochemical Pathway Of Cell Respiration Flow Chart Lovely 25 Best ...
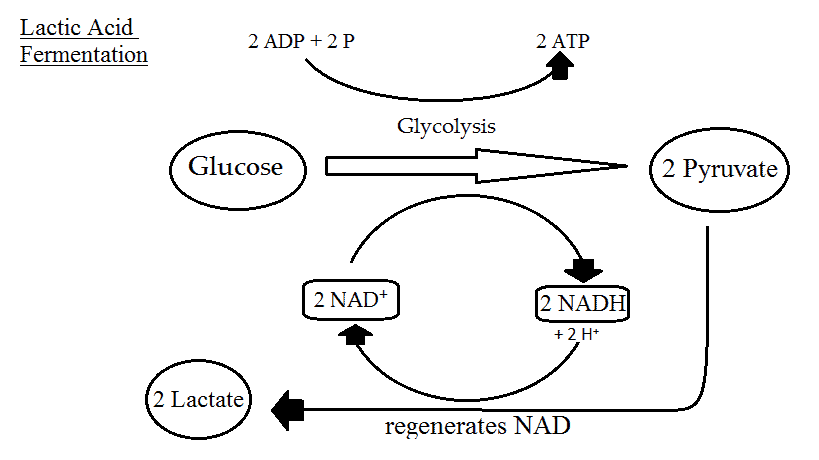
Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams

Model for fermentation and EET-dependent respiration metabolism in E ...

CELLULAR METABOLISM AND FERMENTATION
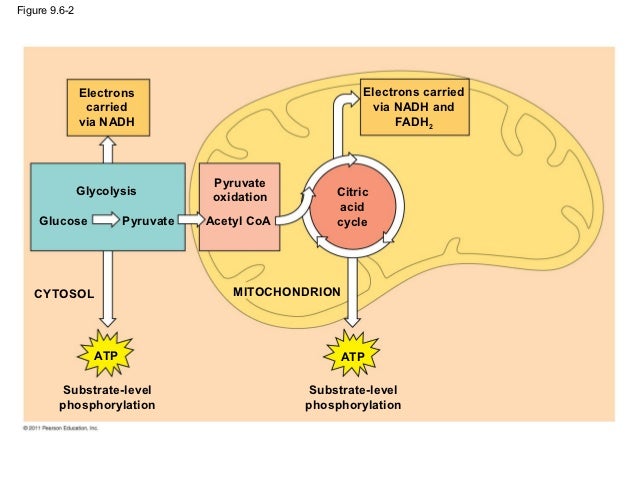
cellular respiration and fermentation
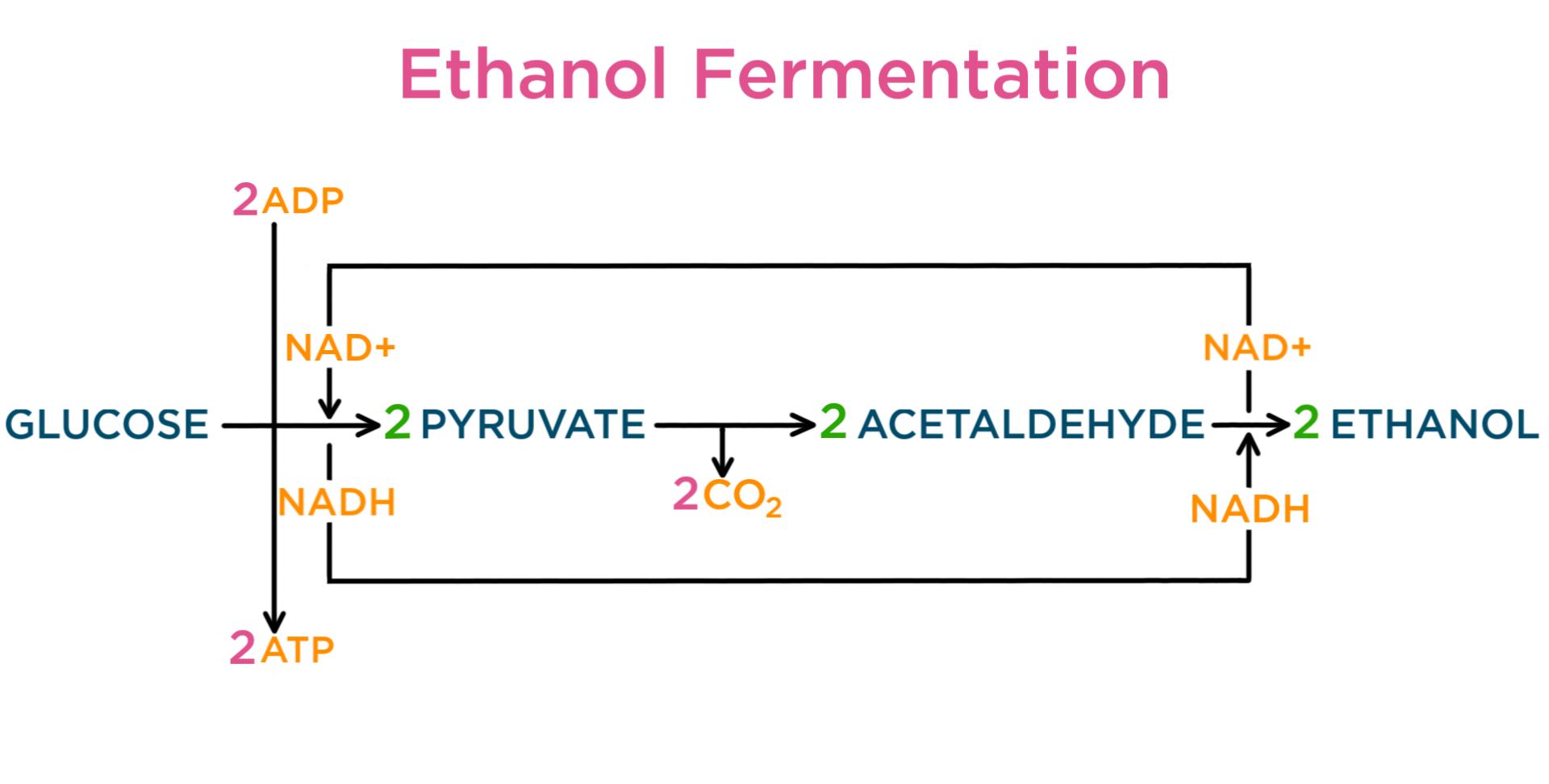
Fermentation — Definition & Role in Cellular Respiration

Alcohol Fermentation
Aerobic Respiration in Cells
PPT

Metabolic pathway and key genes of butanol fermentation. ack, acetate ...
Anaerobic Respiration Vector Illustration Glycolysis And Fermentation ...

Bundle all 3 of my animated PowerPoints regarding cellular respiration ...

Bio Geo Nerd: Metabolic pathways

basics of cellular fermentation and anaerobic pathways
34.2B: Food Energy and ATP
Fermentation — Mathwizurd

Simplified scheme of the cellular metabolism pathways important for AML ...

Metabolic pathways implicated in pyruvate fermentation by S. oneidensis ...
respiration.html 09_06CellRespiration.jpg

Metabolic pathway of 2 3-butanediol fermentation in bacteria Integrated ...

Cellular Respiration Steps And Location

Major metabolic pathways in normal differentiated cells and cancer ...
Metabolic Map Gallery: Common Glycolytic Variants and Fermentation Schemes
PPT
Fermentation and Aerobic Respiration Compared

CELLULAR METABOLISM AND FERMENTATION

Comparison of Photosynthesis and Respiration Processes. Note the ...
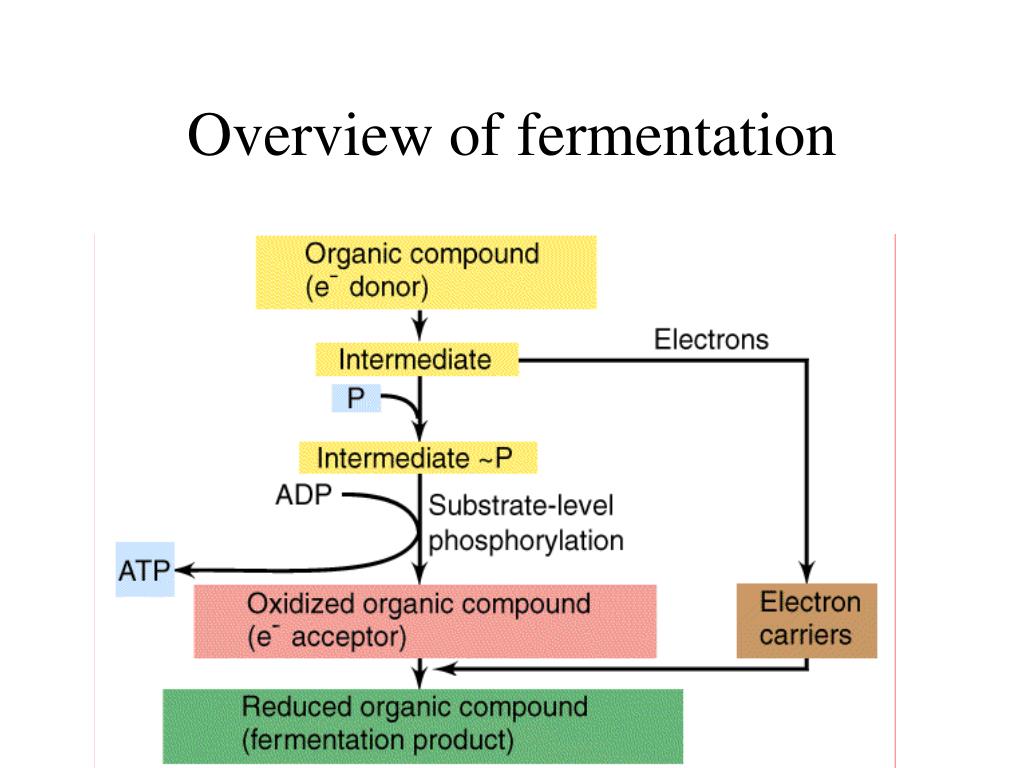
PPT

Yeast energy metabolism. Yeasts have two pathways for ATP production ...
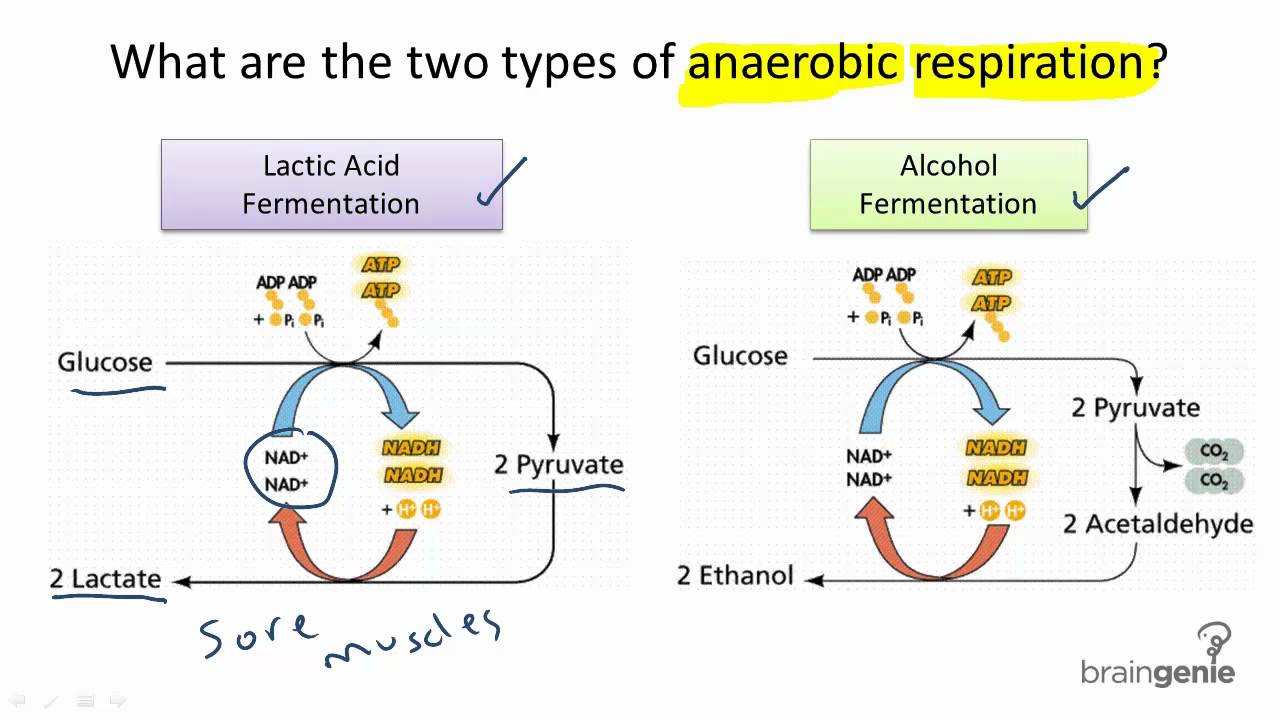
3.1.6 What are the two types of anaerobic respiration
Biochemical pathways of glycolysis, alcoholic fermentation, respiration ...

Regulation of cellular respiration
A general overview of the major metabolic pathways
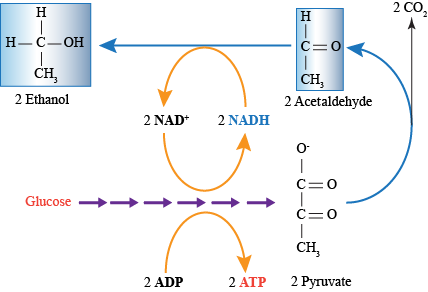
Biology Fermentation and Anaerobic Respiration
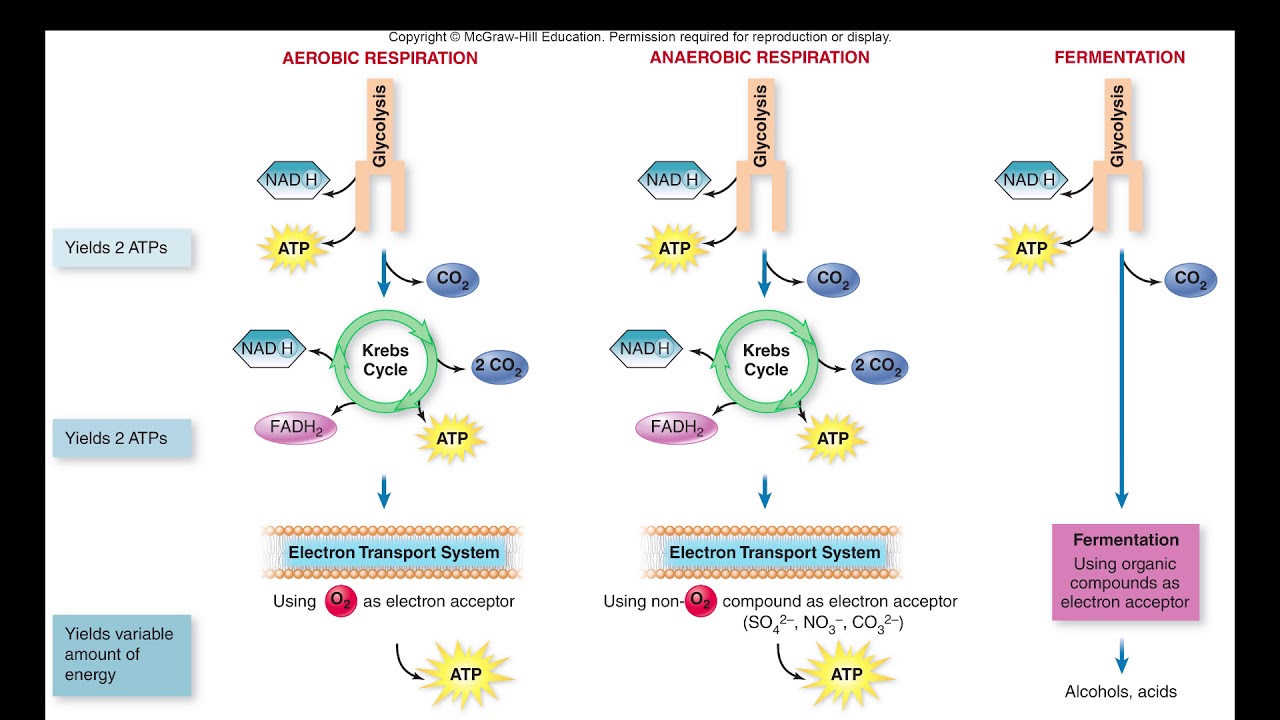
Cellular Respiration vs Anaerobic Energy Production vs Fermentation ...
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] - Ca36ea44ec9c077eD289b81b264b3e00 [BKEYWORD-0-3] - Ca36ea44ec9c077eD289b81b264b3e00](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d67/ca36ea44ec9c077ed289b81b264b3e00.jpg)
[BKEYWORD-0-3]
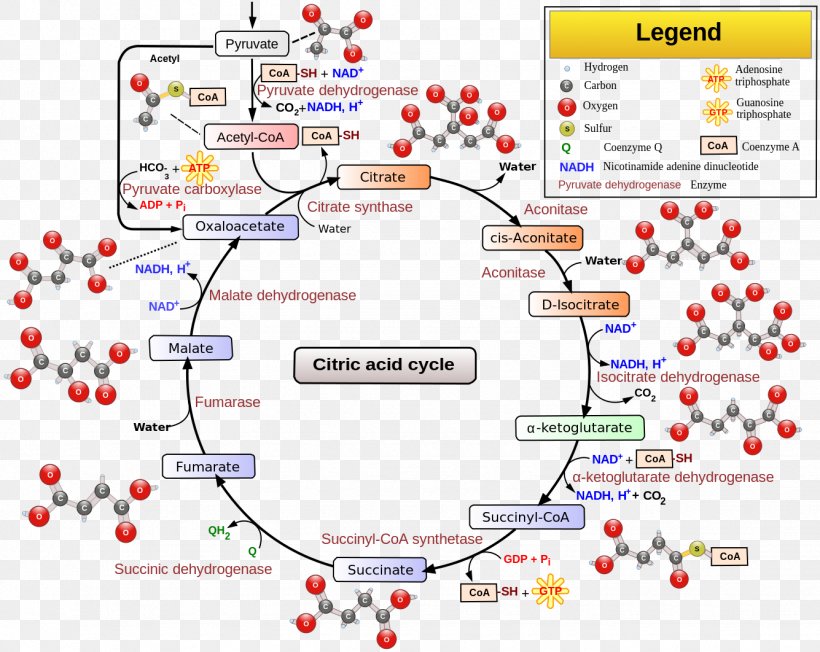
Citric Acid Cycle Cellular Respiration Metabolic Pathway Acetyl-CoA ...
Respiration vs. Fermentation

Biochemical pathways of glucose and lactate fermentation by ...
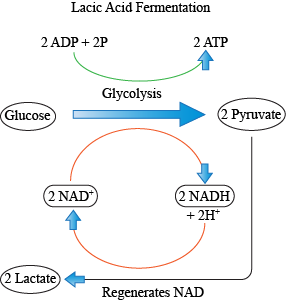
Fermentation and Anaerobic Respiration
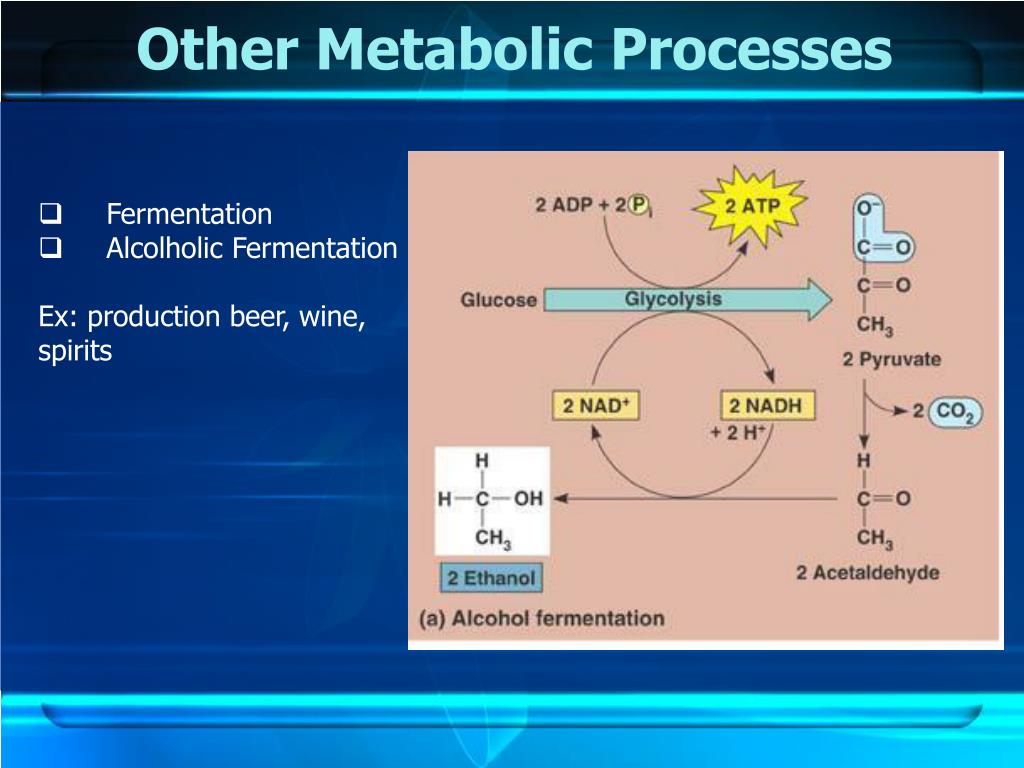
PPT

2: The pathways involved in respiration and fermentation. [Hellborg and ...

the three basic catabolic pathways are

38 Cells

BIOL 102 Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration and Fermentation

transition phase p. 1

Cellular Respiration





Kommentare
Kommentar veröffentlichen